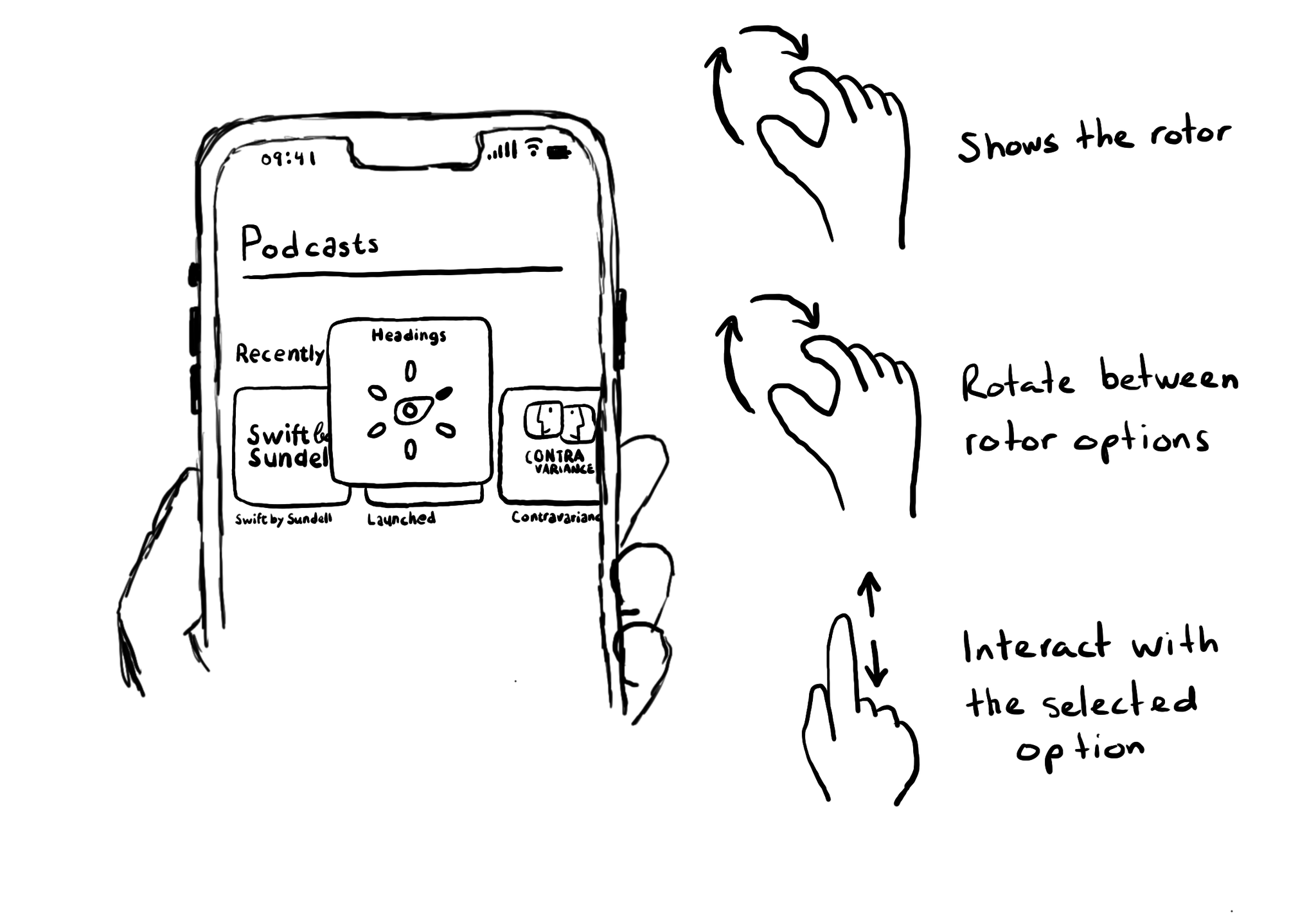
Optimising for navigation by making a view accessible shouldn’t come at the expense of the buttons in it not being accessible. Configuring custom actions will allow the user to access them using the Actions rotor.
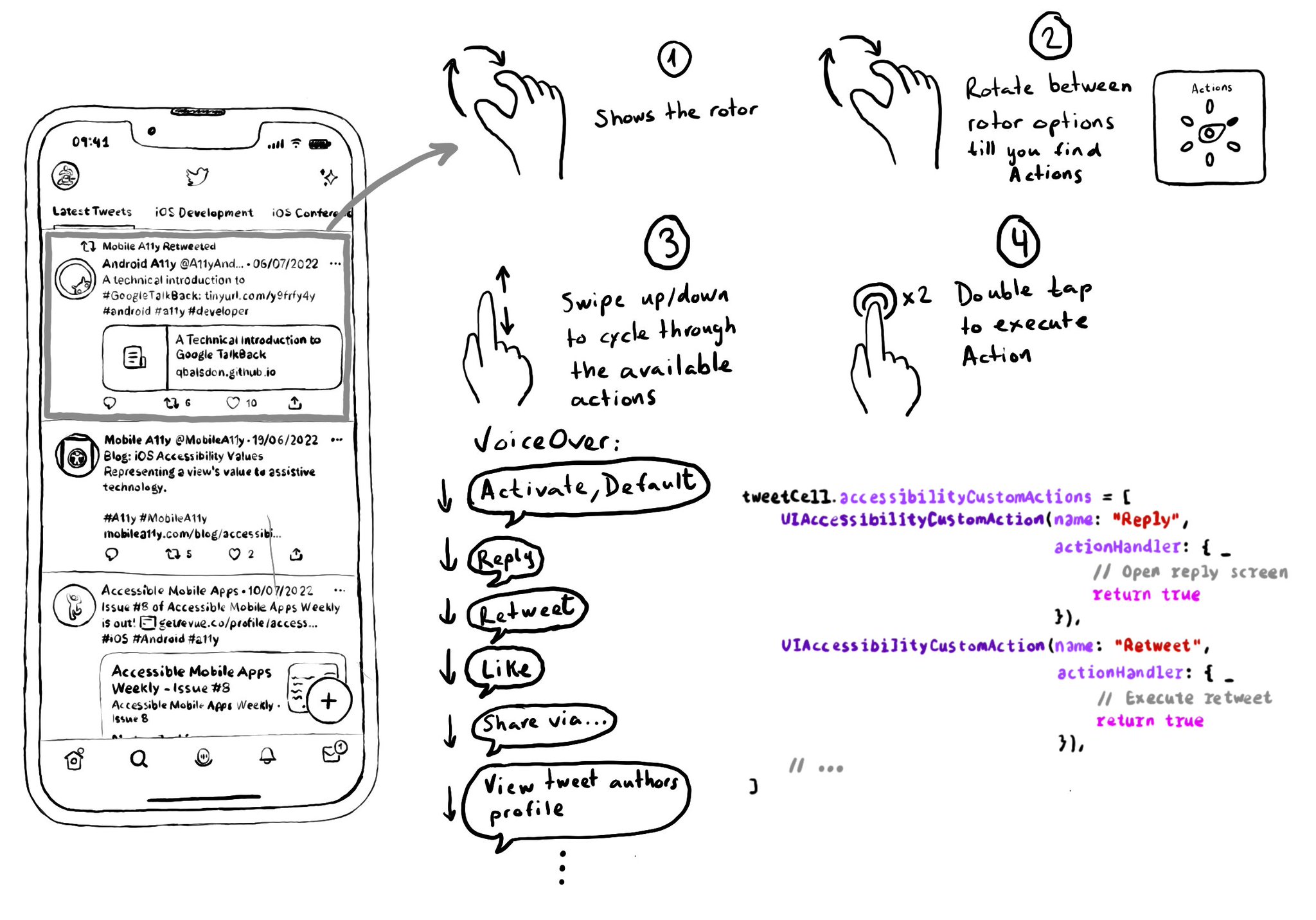
With the Actions rotor, users can swipe up and down to cycle through all the options, stop at the desired one, and double tap to execute that action.
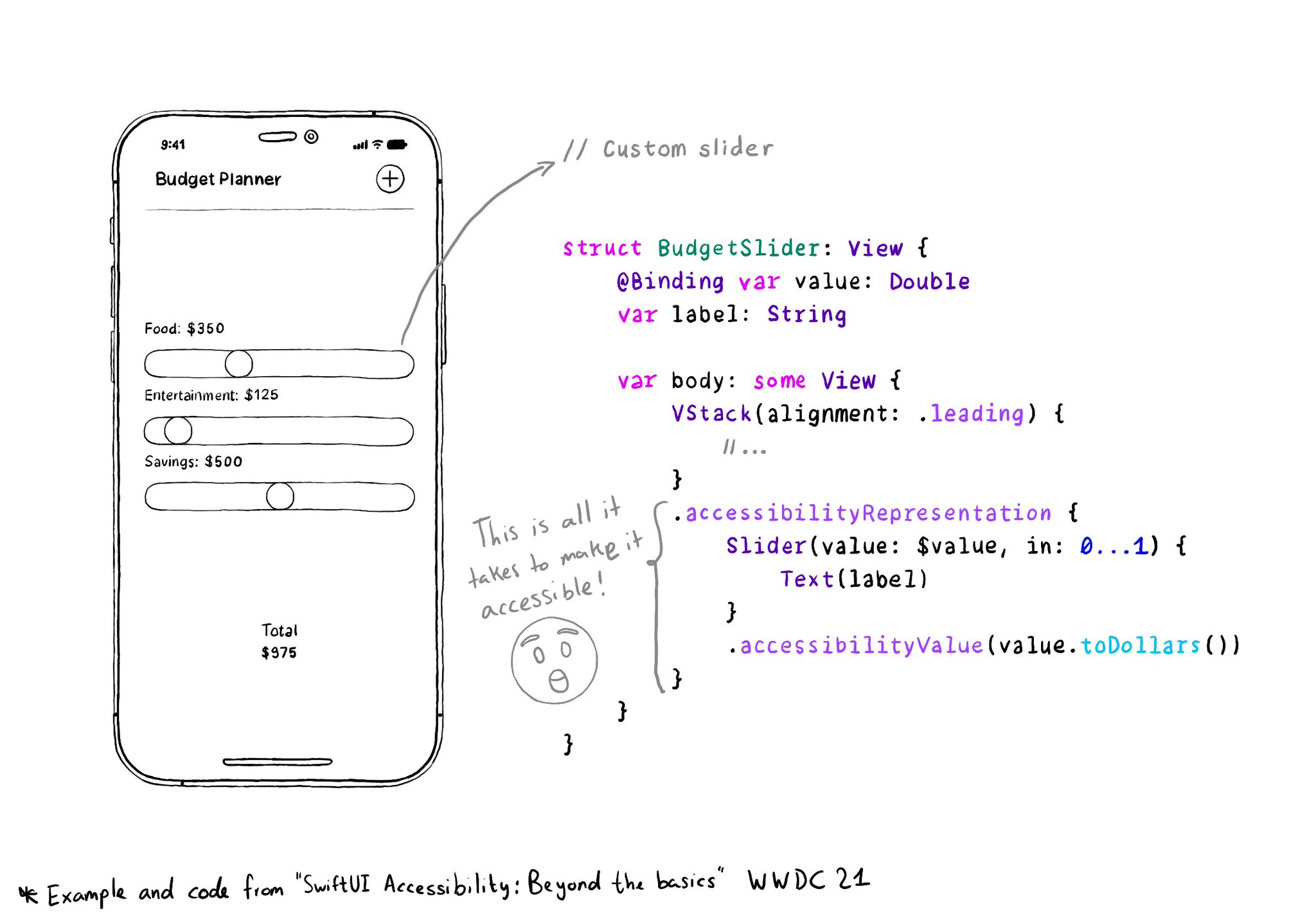
You can configure an array of custom actions. Custom actions can have a name that will be announced by VoiceOver and an action handler or target selector with the code that will be executed.
https://developer.apple.com/documentation/objectivec/nsobject-swift.class/accessibilitycustomactions