Custom actions are also great for actions that are executed with a gesture that is overridden by VoiceOver. Think of the unread, flag and archive hidden options that you can make visible by swiping left/right on a message row in the Mail app.
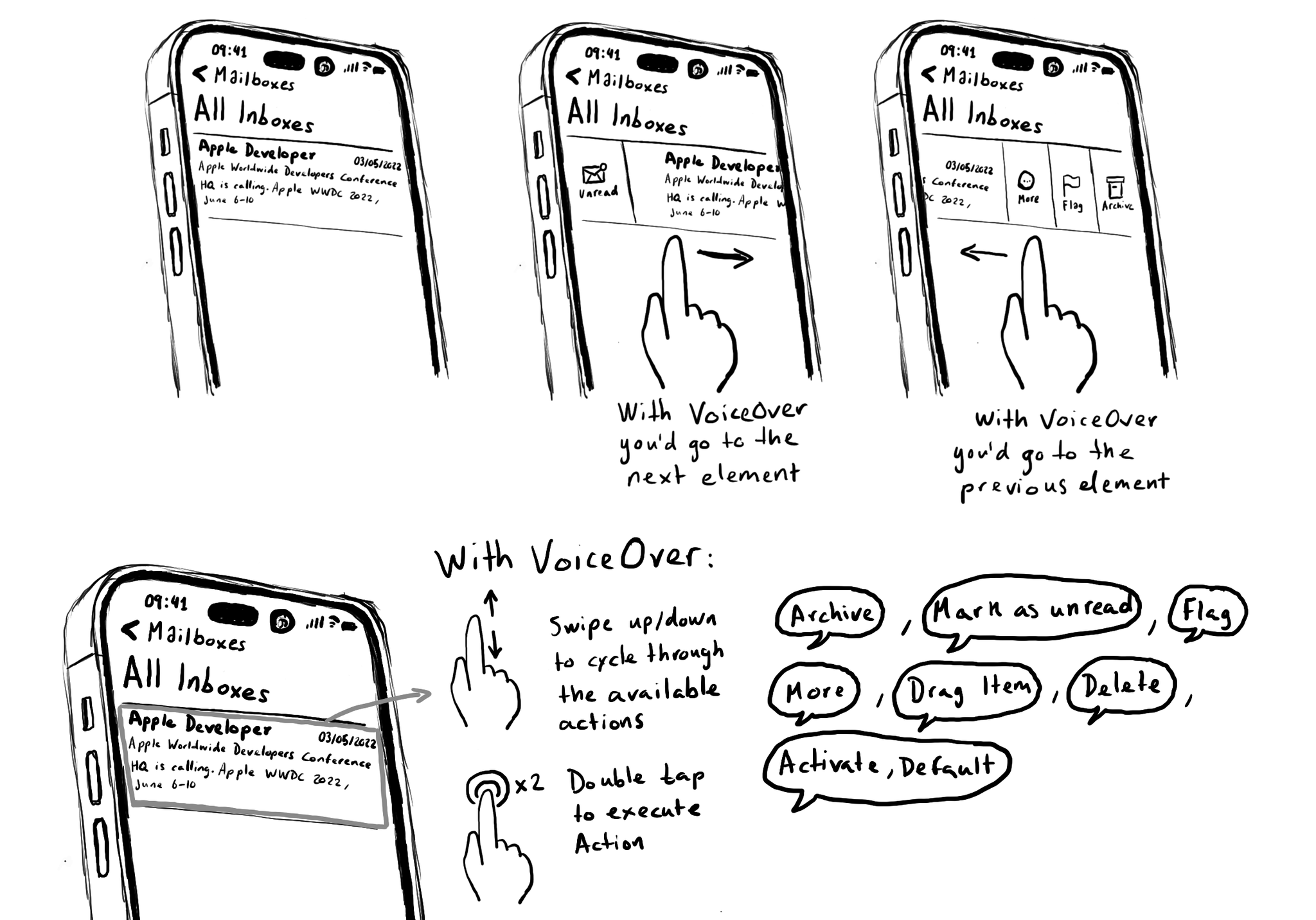
Custom actions are also great for actions that are executed with a gesture that is overridden by VoiceOver. Think of the unread, flag and archive hidden options that you can make visible by swiping left/right on a message row in the Mail app.

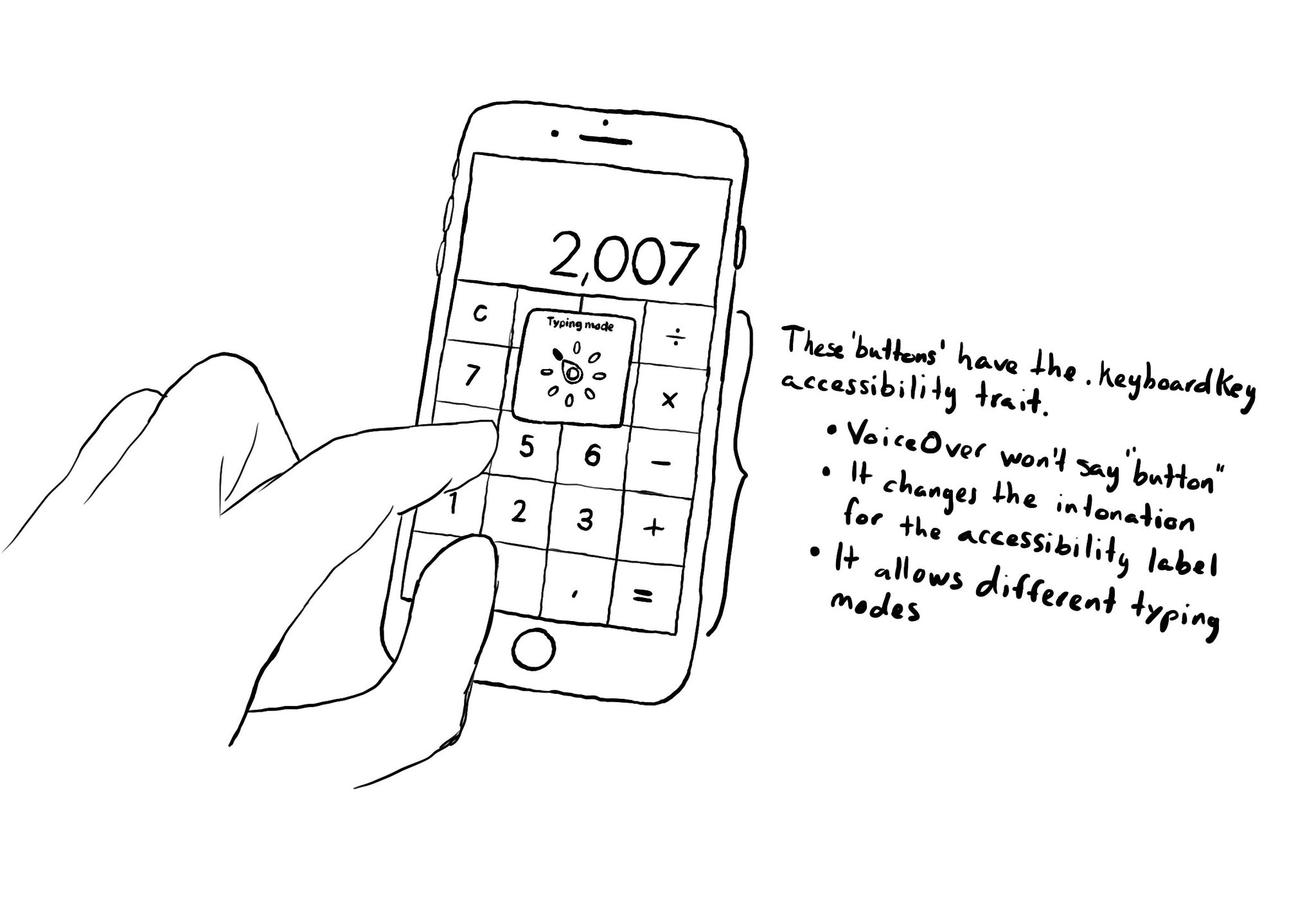
There is an accessibility trait for defining something that represents a custom keyboard's key: .keyboardKey. It allows VoiceOver users to change the typing mode to Direct touch typing. The calculator app or an access pin pad, are some examples.
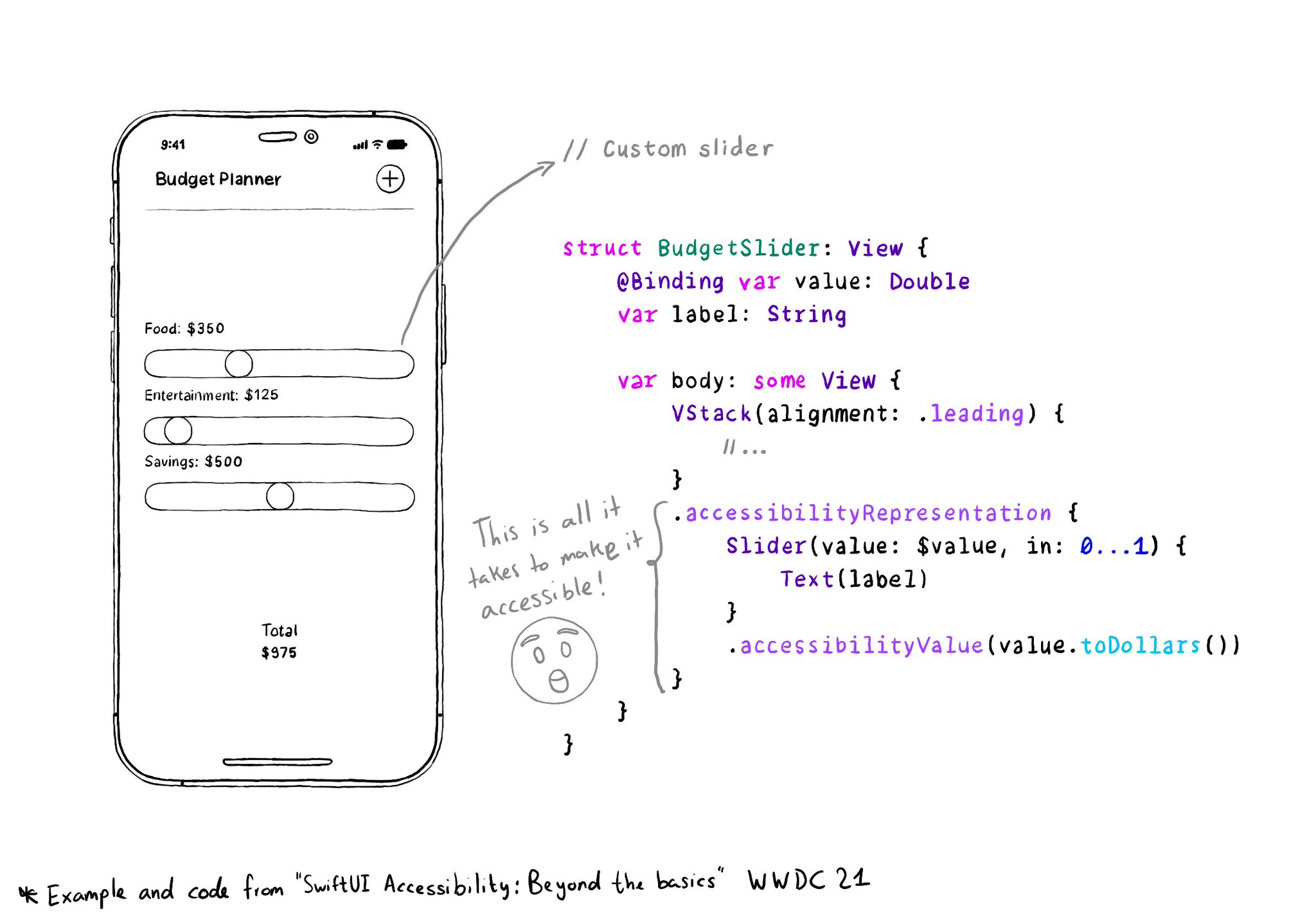
With accessibilityRepresentation(representation:), you can create a custom component and it can be perceived by assistive technologies as the view you pass as representation. No need to manually configure accessibility attributes. It is one of the most interesting additions to SwiftUI to help you develop accessible UI components. If your custom component behaves similarly to a native one, this is the way to go. https://developer.apple.com/documentation/swiftui/view/accessibilityrepresentation(representation:)
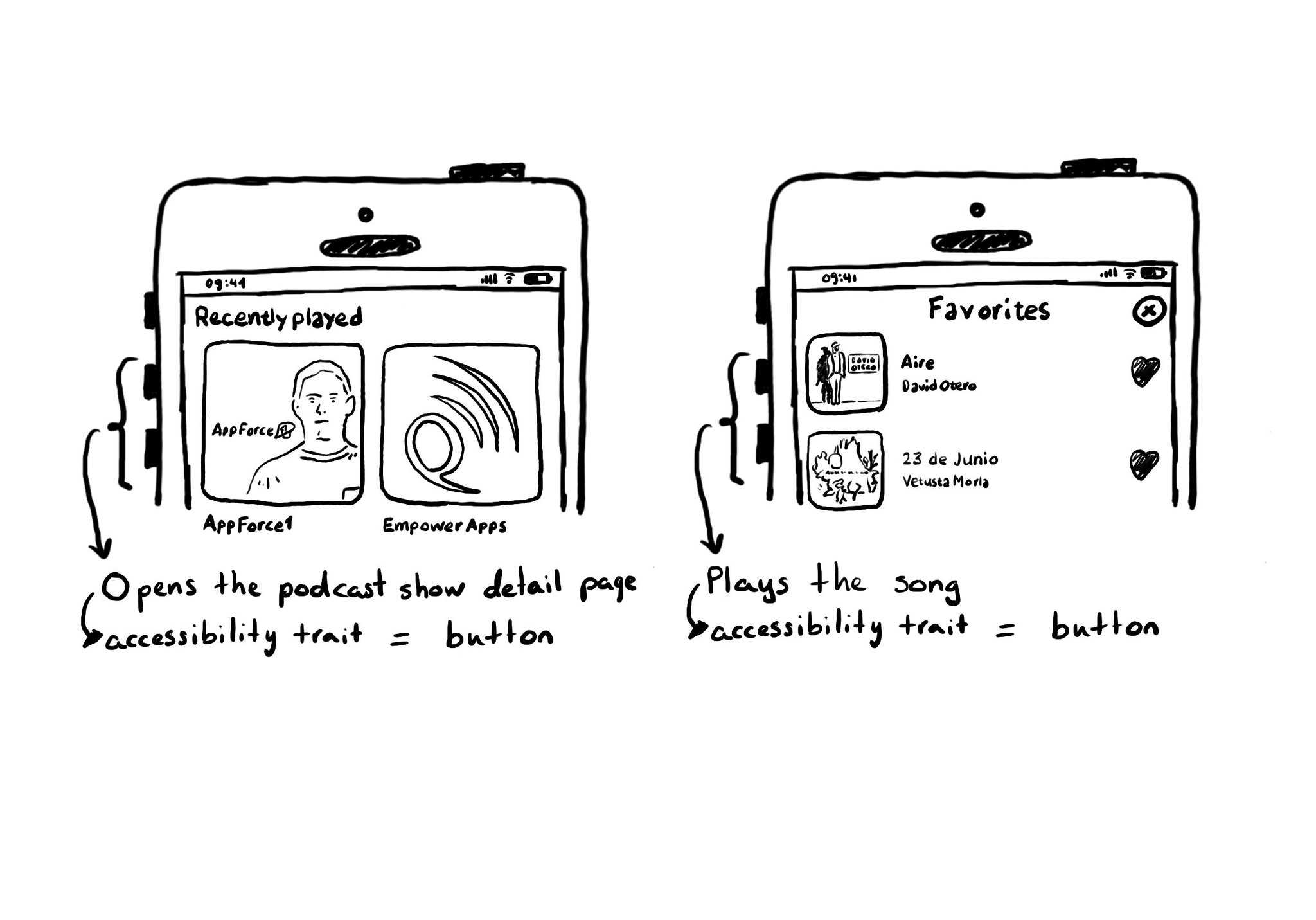
A common example where you need to manually configure the button accessibility trait is for some table/collection view cells. These tend to be “buttons” that perform an action, like playing music, or bring the user to a different screen.
Content © Daniel Devesa Derksen-Staats — Accessibility up to 11!