What is the difference between isAccessibilityElement and accessibilityElementsHidden? The first one makes the view not accessible, but its subviews can still be accessible. The second one hides the view and all its subviews from assistive tech.
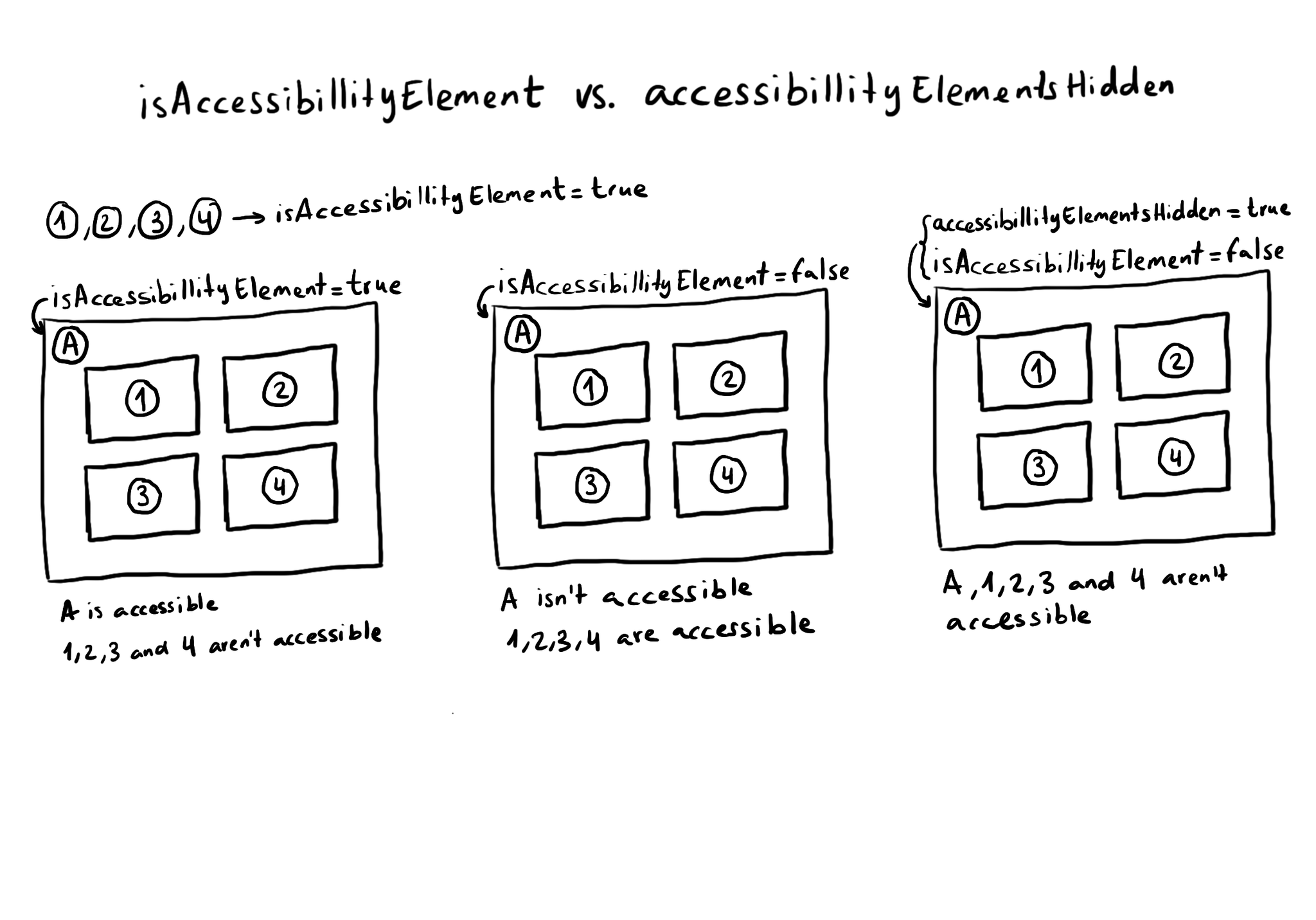
What is the difference between isAccessibilityElement and accessibilityElementsHidden? The first one makes the view not accessible, but its subviews can still be accessible. The second one hides the view and all its subviews from assistive tech.

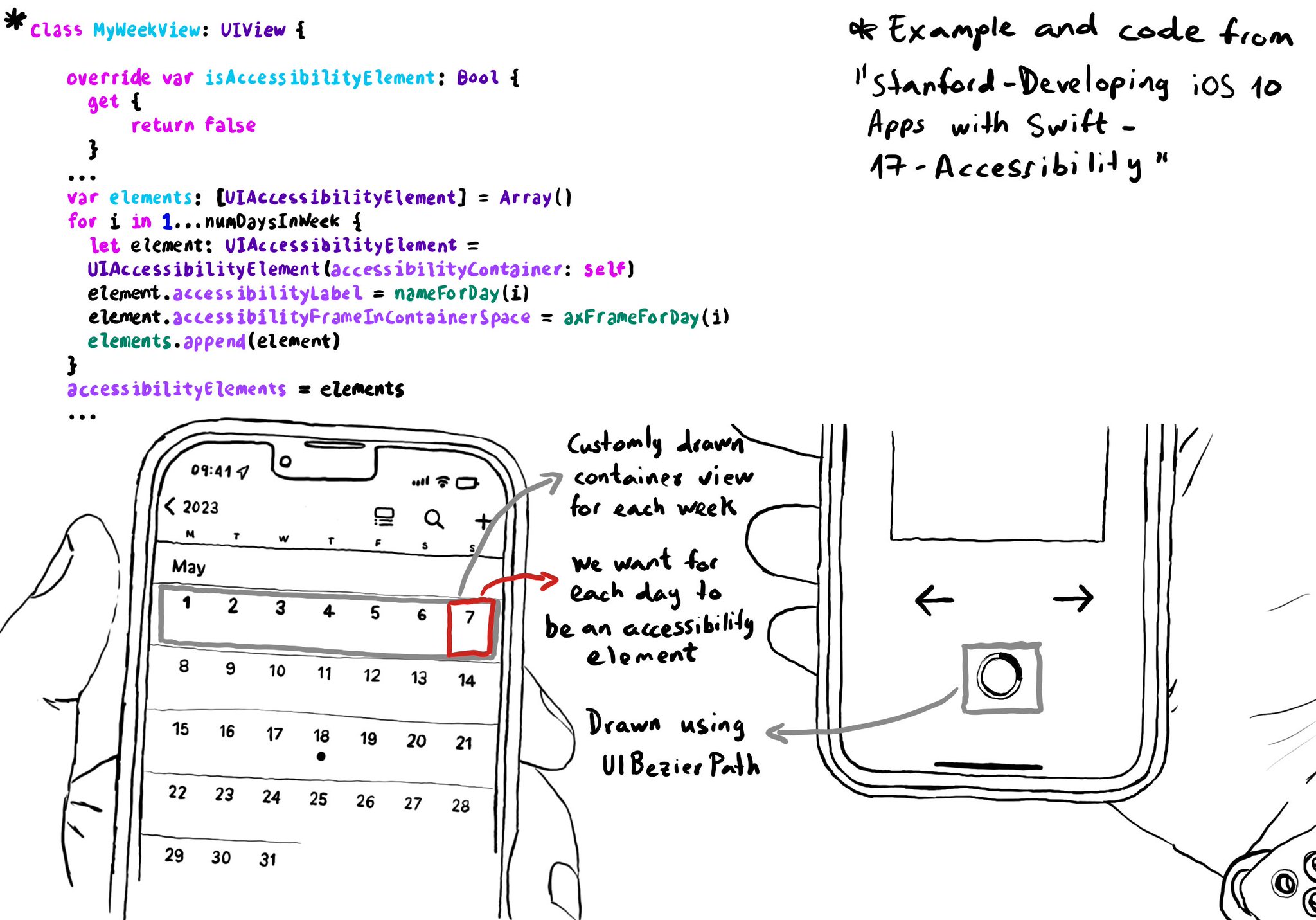
You can create your own accessibility elements from scratch. One use-case for doing that is when you do some custom drawing instead of building your UI using or relying on UIKit components. A circular progress bar, could be an example.
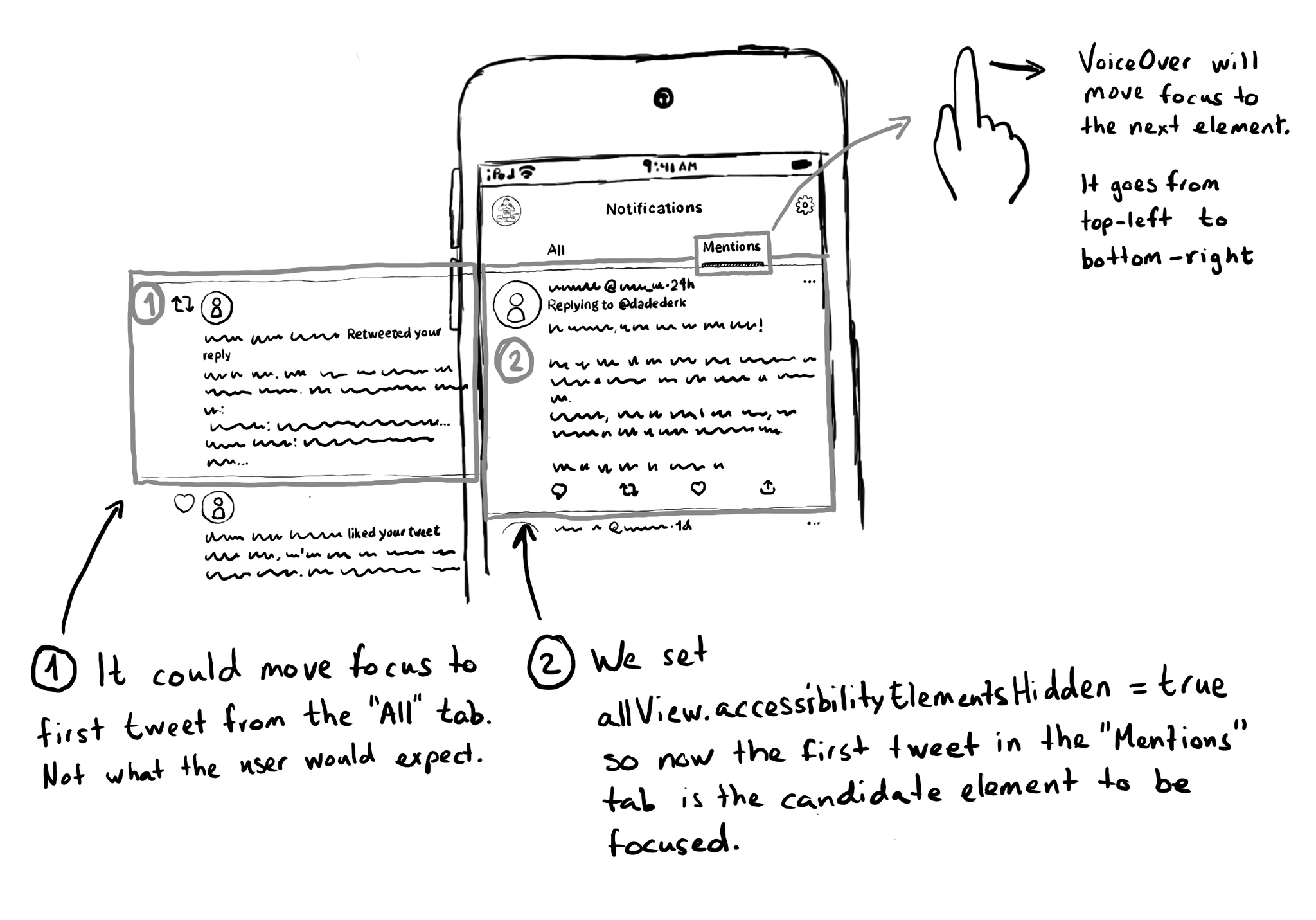
If you need for a view (and all its subviews) not to be focusable by assistive tech like VoiceOver, you can set its accessibilityElementsHidden property to true. This isn't needed very often, but it can be useful for certain custom experiences.
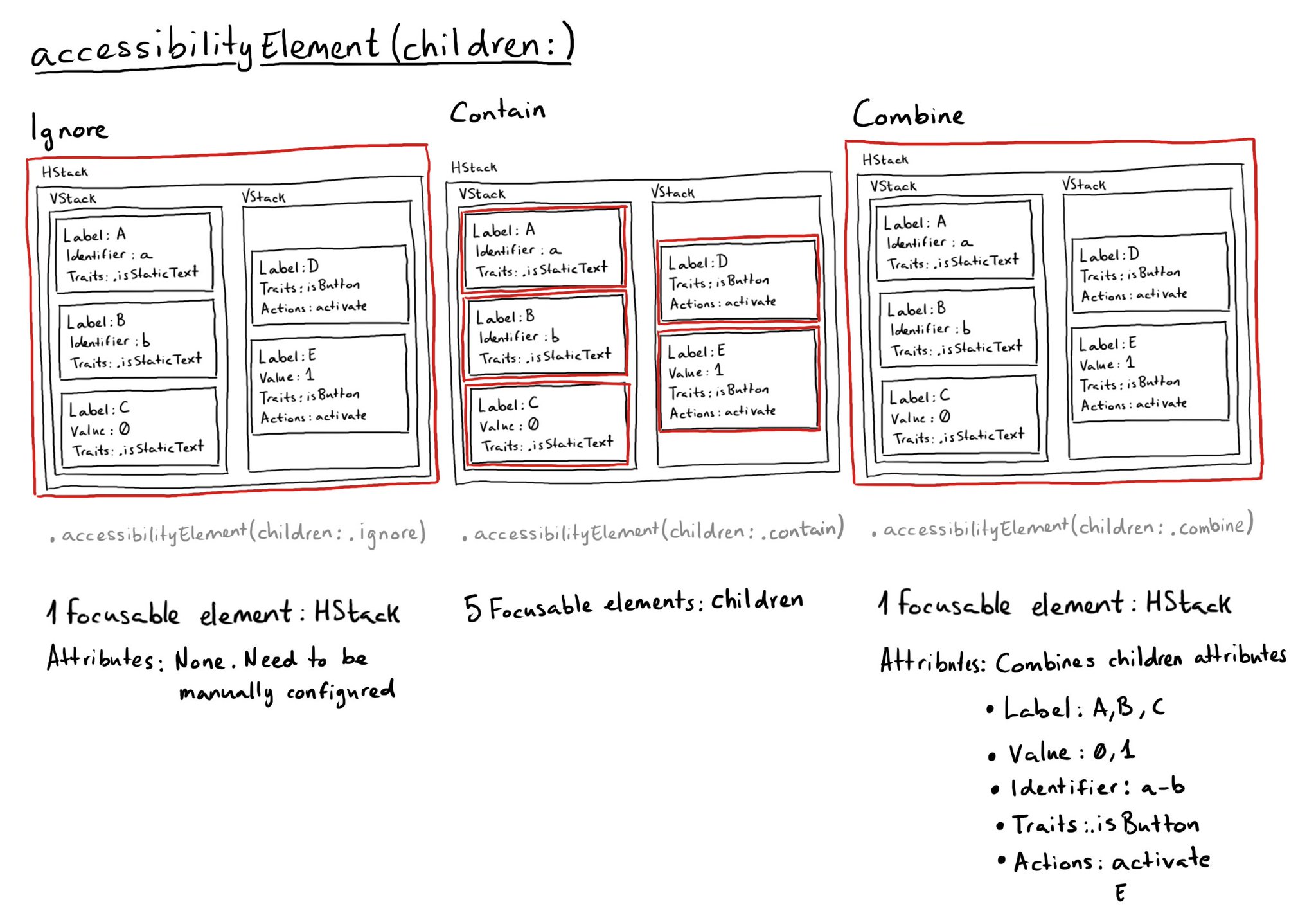
In SwiftUI there is a very useful modifier accessibilityElement(children:), that will do very different things depending on the AccessibilityChildBehavior passed as a parameter. There are three options: ignore (default), contain, and combine.
Content © Daniel Devesa Derksen-Staats — Accessibility up to 11!