If you need for a view (and all its subviews) not to be focusable by assistive tech like VoiceOver, you can set its accessibilityElementsHidden property to true. This isn't needed very often, but it can be useful for certain custom experiences.
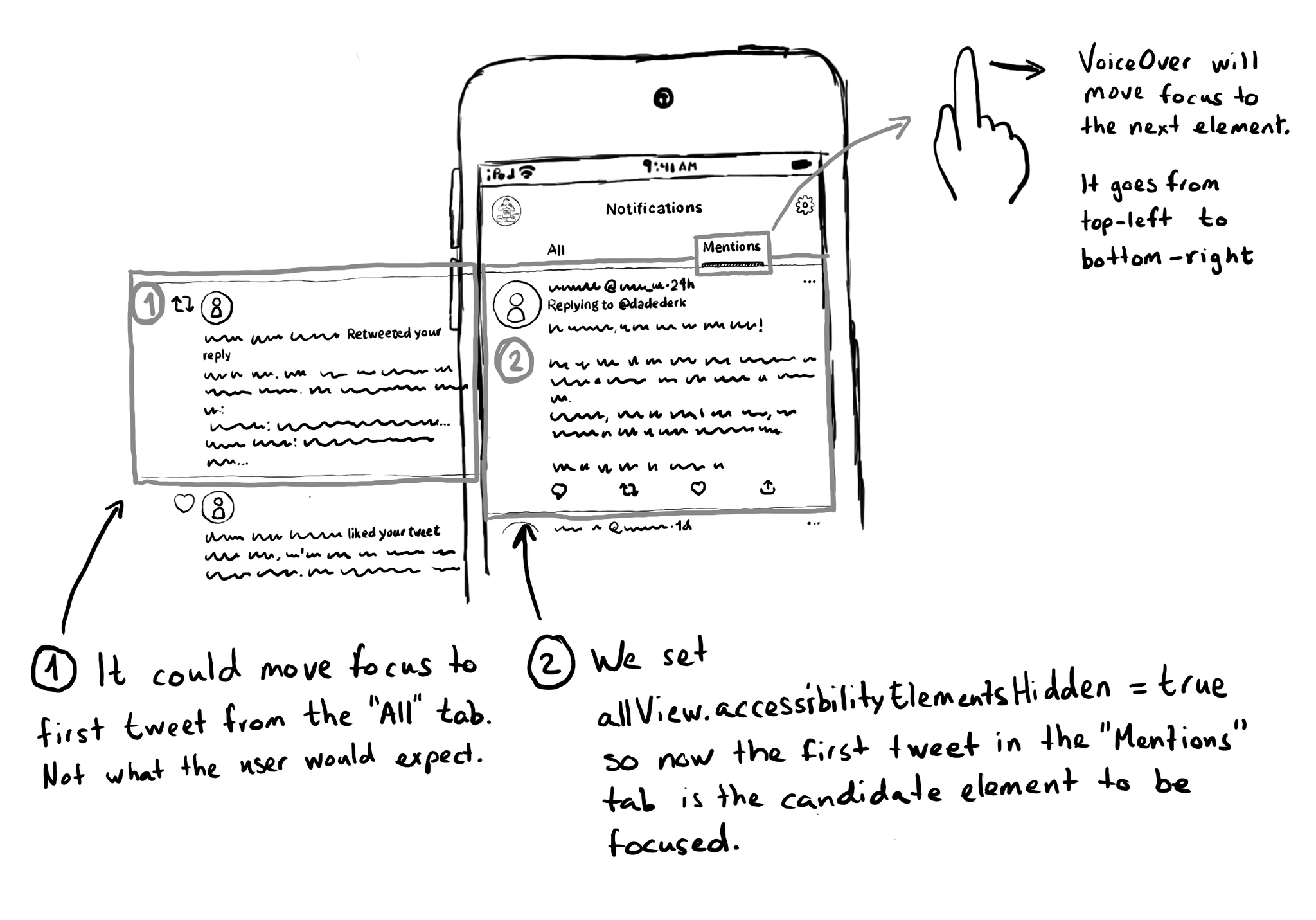
If you need for a view (and all its subviews) not to be focusable by assistive tech like VoiceOver, you can set its accessibilityElementsHidden property to true. This isn't needed very often, but it can be useful for certain custom experiences.

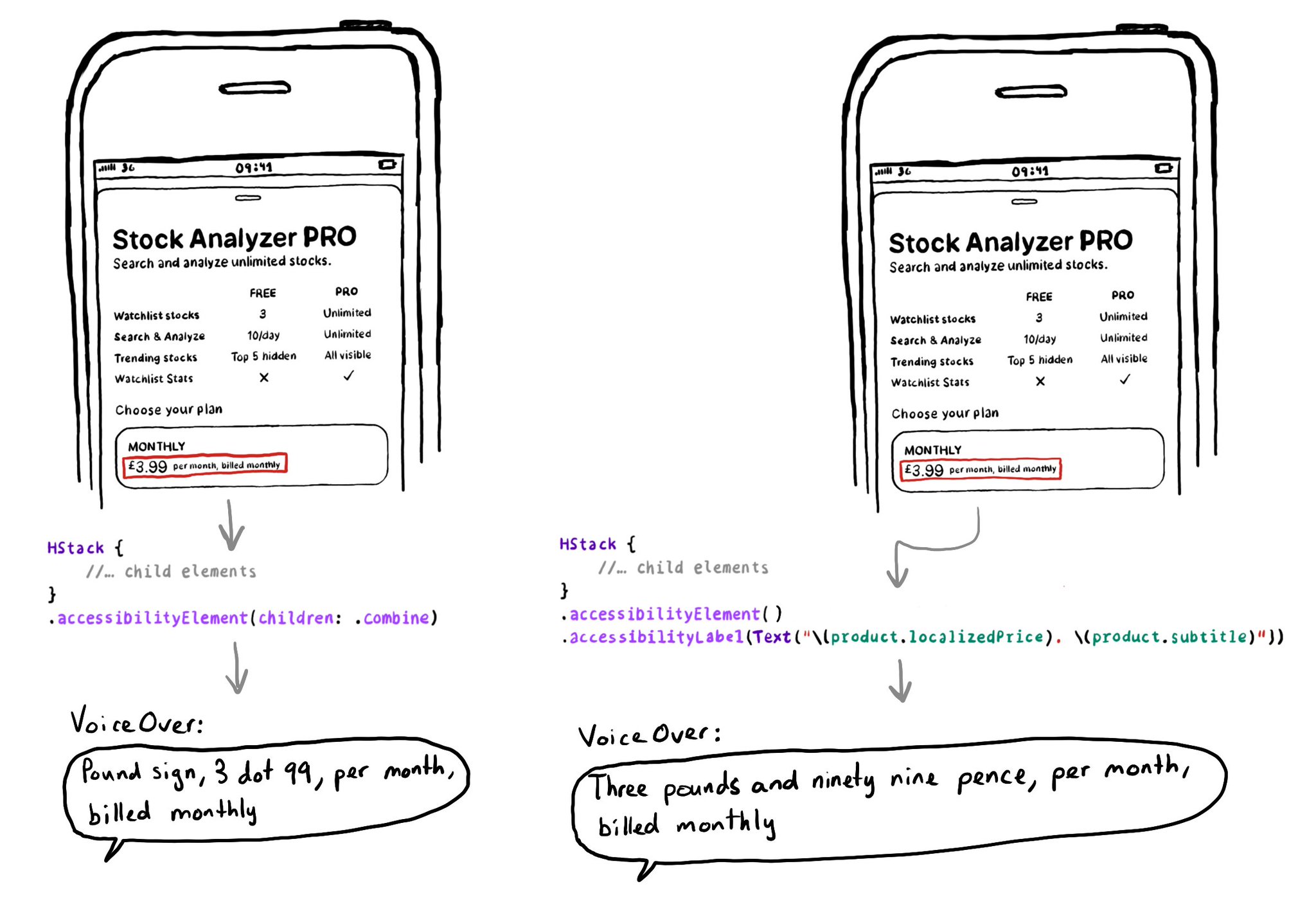
The .accessibilityElement(children: ) modifier with the .ignore argument does a similar thing to set the container view to be an accessibility element in UIKit. It is the default argument, so you can just say .accessibilityElement(). Because of this, you'll need to use other modifiers to make it accessible and manually configure an accessibility label and value, traits... when necessary. https://developer.apple.com/documentation/swiftui/view/accessibilityelement(children:) https://developer.apple.com/documentation/swiftui/accessibilitychildbehavior/ignore
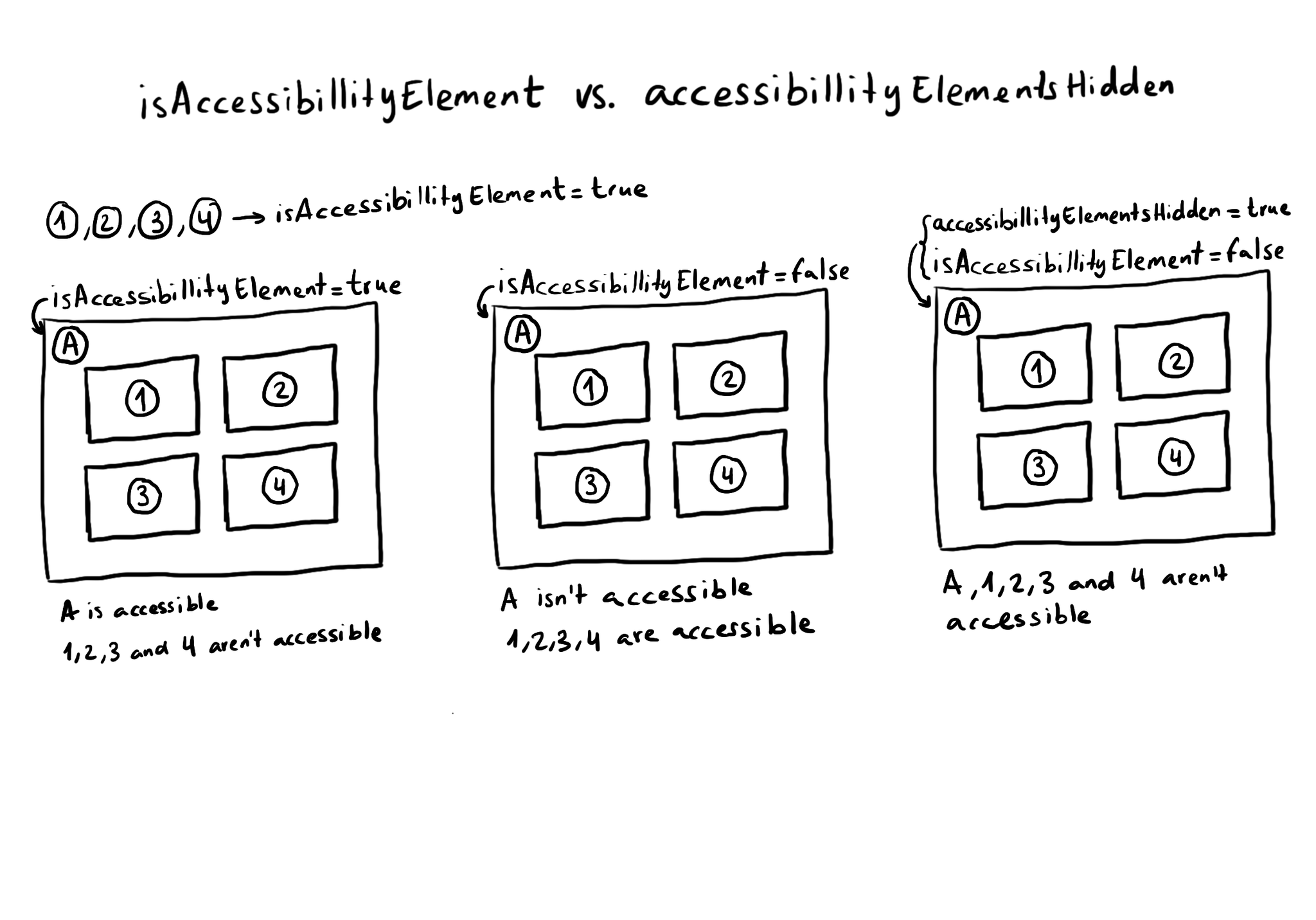
What is the difference between isAccessibilityElement and accessibilityElementsHidden? The first one makes the view not accessible, but its subviews can still be accessible. The second one hides the view and all its subviews from assistive tech.
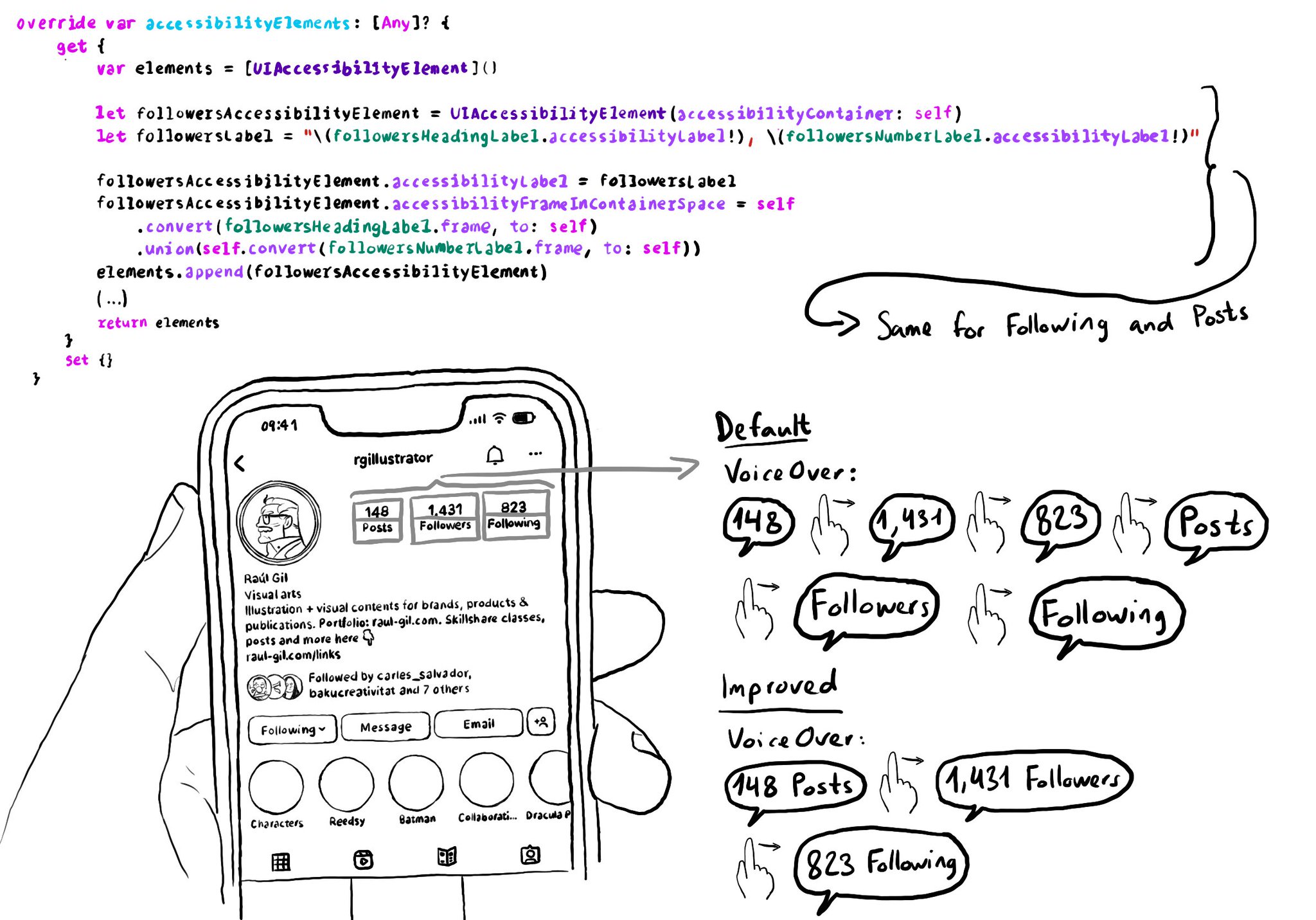
Sometimes you can create your own accessibility elements from scratch to group elements too. Perhaps because they're not contained in the same superview. You can combine these elements' frames and provide a suitable accessibility label.
Content © Daniel Devesa Derksen-Staats — Accessibility up to 11!