Have you used Voice Control? It feels like magic! But it would be cool if you could have an easier time guessing the name of a button without the “Show names” command. We can do that! Meet accessibilityUserInputLabels.
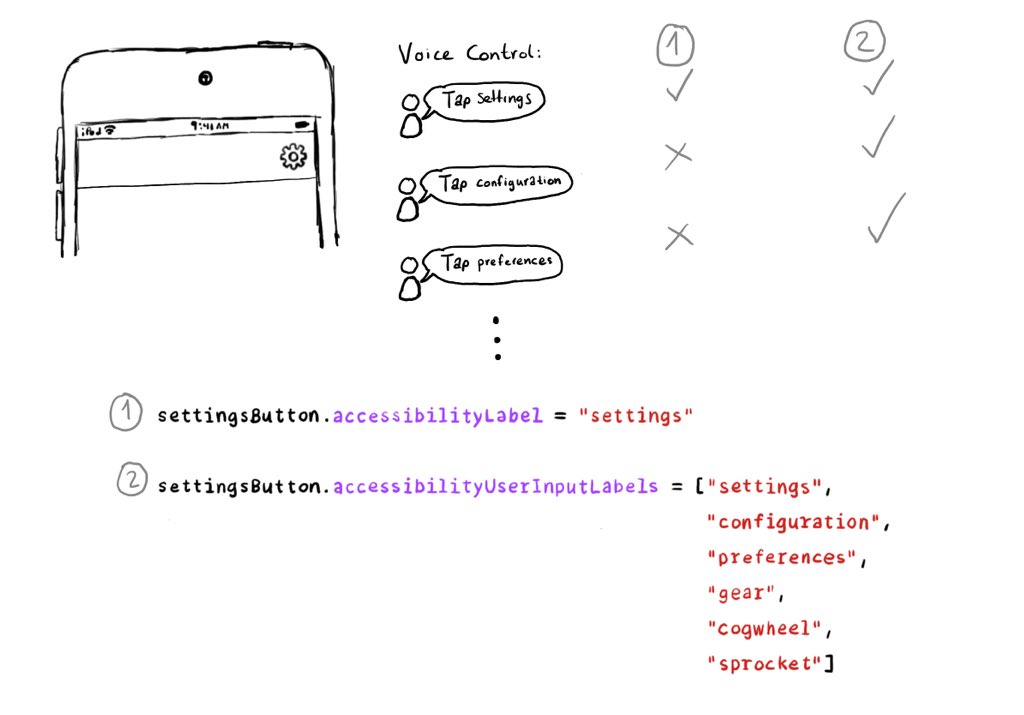
Have you used Voice Control? It feels like magic! But it would be cool if you could have an easier time guessing the name of a button without the “Show names” command. We can do that! Meet accessibilityUserInputLabels.

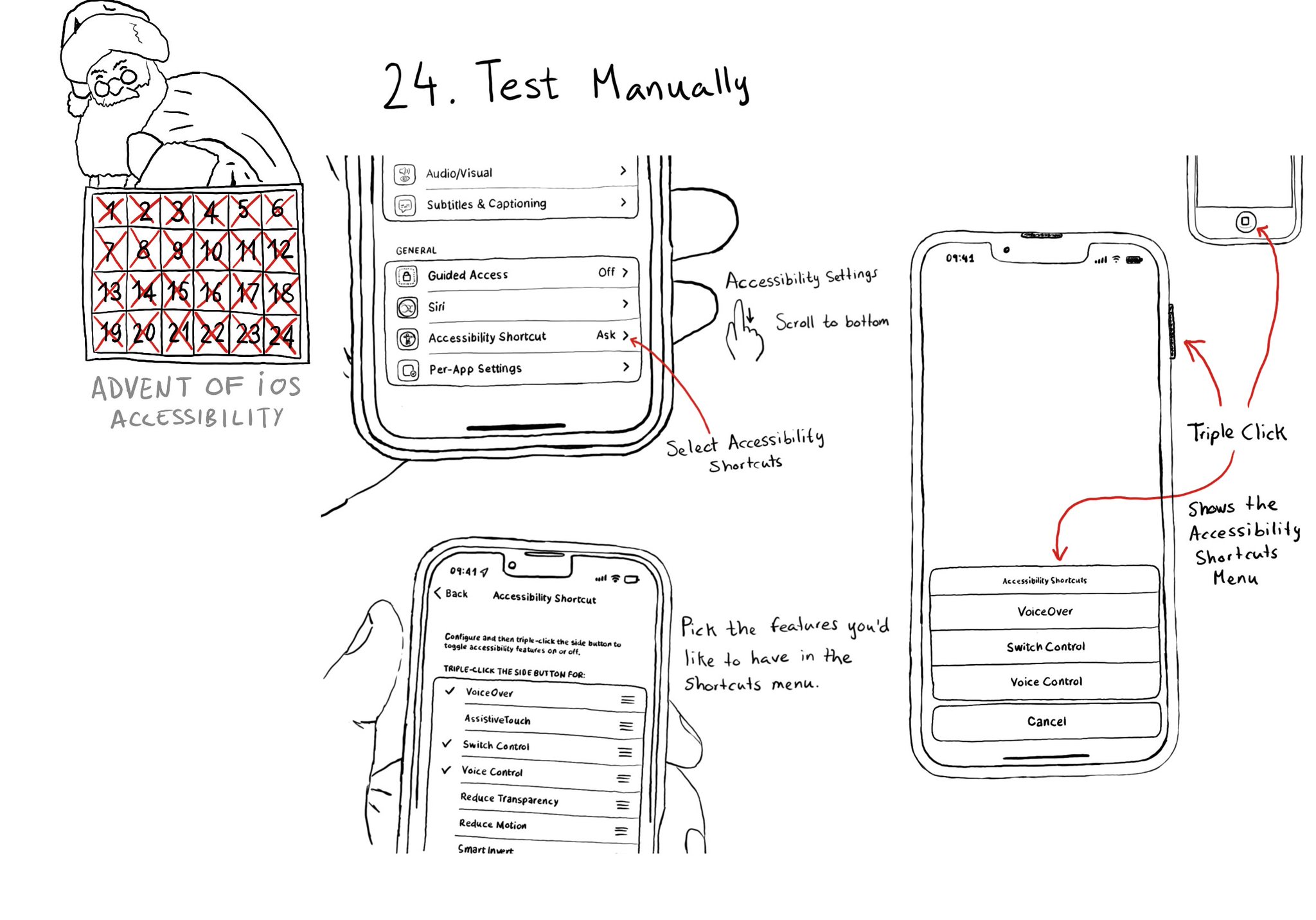
Test manually. Familiarise yourself with different assistive technologies. I find it useful to start with VoiceOver but check out Voice Control, Full Keyboard Access, and others... Remove friction, configuring shortcuts can help. Merry Christmas!

Accessibility labels might not be the best input labels, used for example to find or interact with elements with Voice Control or Full Keyboard Access. In those cases, you can provide accessibility user input labels.
Check isReduceTransparencyEnabled to lower transparency. A great example is Spotlight. Not only transparency is removed but it keeps the main color of the background, it feels personalized and contextual but reduces noise and improves contrast.
Content © Daniel Devesa Derksen-Staats — Accessibility up to 11!